Ancient Empires
Old Kingdom
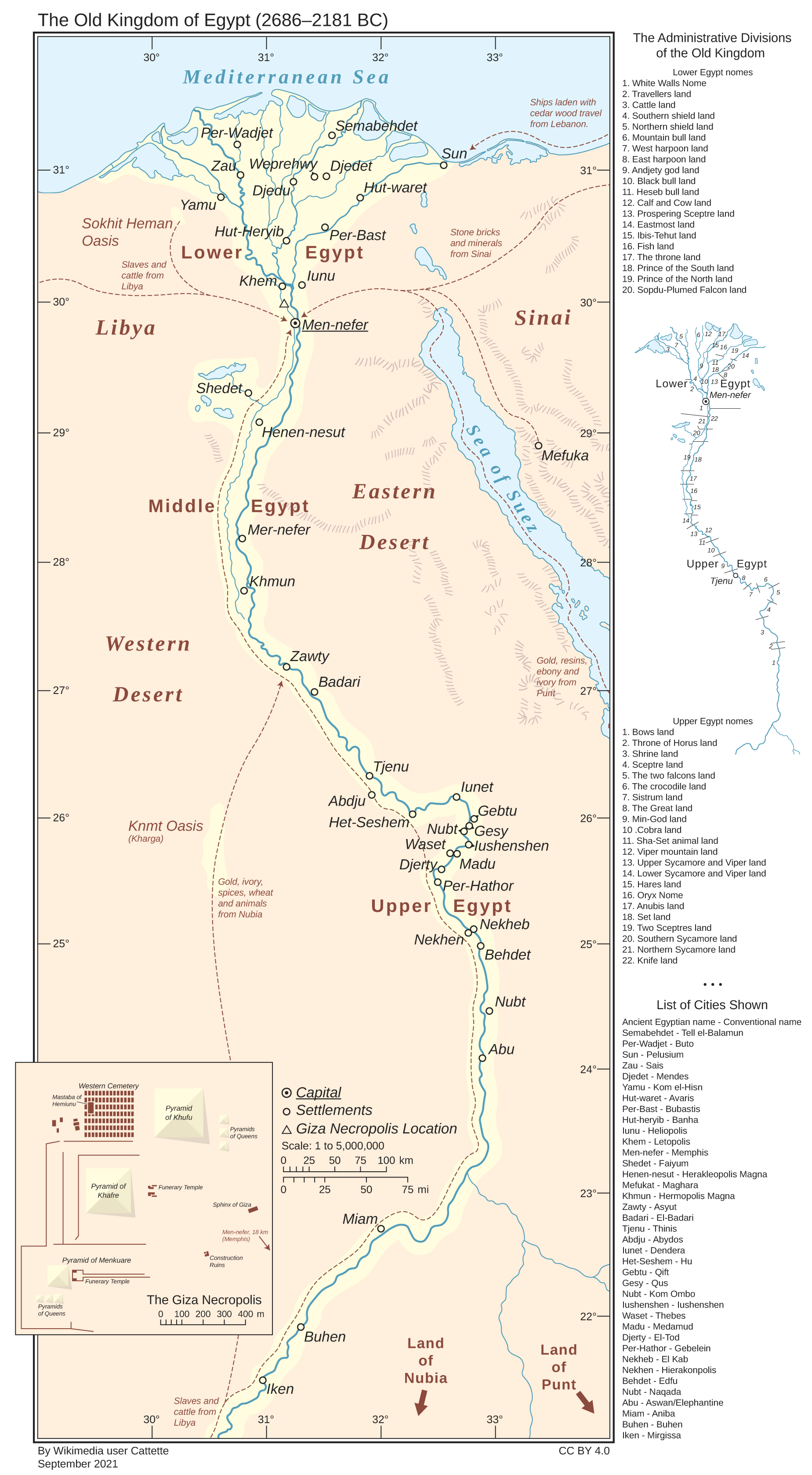
The Old Kingdom of Egypt (c. 2649 - 2134 BC), also known as the "Age of the Pyramids," encompassed the reigns of King Sneferu, who perfected the art of pyramid-building, as well as kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who constructed the pyramids at Giza.
Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire (c. 2334 – 2154 BC) was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia after the long-lived civilization of Sumer. It was centered in the city of Akkad and united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rule. Sargon was the empire's first ruler, ca 2300 BC.

The Akkadian Empire was replaced by Assyria in the north and Babylonia in the south.
Assyria (c. 2025 – 609 BC) existed as a city-state, a territorial state, and eventually an empire.
Old Babylonian Empire
The Old Babylonian Empire (c. 1894 – 1595 BC) emerged after the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur (Summerian). King Hammurabi ruled Babylon from 1792 to 1750 BC.
New Kingdom
The New Kingdom (ca 1570 - 1069 BC), also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, marked the peak of Egypt's power. Some of Egypt's most famous kings reigned during this time, including Ahmose I, Hatshepsut, Thutmose III, Amenhotep III, Akhenaten, and Tutankhamun.

Hittites
The Hittites were an Anatolian people who established an empire centered on Hattusa in north-central Anatolia. This empire reached its height during the rule of Suppiluliuma I (c. 1350–1300 BC).

Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire (911 – 609 BC) grew to dominate the ancient Near East throughout much of the 8th and 7th centuries BC, becoming the largest empire in history up to that point.
Ashurbanipal was the last great king of Assyria. He is chiefly remembered as a patron of art and literature. He built the Library of Ashurbanipal, which had as many as 100,000 texts at its height. It was not surpassed until the construction of the Library of Alexandria, several centuries later.
Persian Empire
The Persian (Achaemenid) Empire (550 – 330 BC) was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great. It was the greatest empire the world had ever seen at its time.
The empire achieved its territorial peak during the rule of its third king Darius I.
Xerxes I, the son of Darius and the empire's fourth King, invaded Greece in 480 BC. His forces temporarily overran mainland Greece until losses at Salamis and Plataea a year later reversed their gains and ended the second invasion decisively.
Alexander the Great conquered the Persian Empire in 330 BC.
